
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) is an advanced AI architecture that combines the power of large language models (LLMs) with external knowledge retrieval. Here’s a breakdown of RAG, its workings, importance, and business applications:
You’re probably familiar with some of the shortcomings of current AI. For me, the most frustrating aspect is that you can’t rely on it for accurate information. Not only do current LLMs frequently ‘hallucinate’ facts, people, code libraries, events, and more – they state this information with such confidence that it can be hard to spot. This can be reduced with high quality AI training data, and fine tuning, but RAG is another powerful solution.
RAG is a hybrid AI system that enhances traditional language models by incorporating a retrieval step to fetch relevant information from external sources before generating responses. This approach allows AI to access up-to-date, factual information beyond its initial training data.
Key Takeaways
- RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) is an AI architecture that combines large language models (LLMs) with external knowledge retrieval to provide accurate and reliable information.
- This approach minimizes AI “hallucinations,” allows access to up-to-date data, and enhances verifiability by citing sources.
- RAG systems are particularly valuable in business applications such as customer service, knowledge management, and personalized marketing, among others.
- Challenges for RAG include scalability, contextual understanding, and integrating diverse knowledge sources.
- GraphRAG, an advanced RAG variant, uses knowledge graphs to improve context understanding and scalability, showing promise in overcoming traditional RAG limitations.
RAG not only makes AI more reliable, it introduces verifiability – simply put you can click on a link to the source and check it yourself. For example, Perplexity, a RAG application that also combines web search shows a list of sources at the top of the answer, as well as a numbered citation where it has written its response based on a specific source:

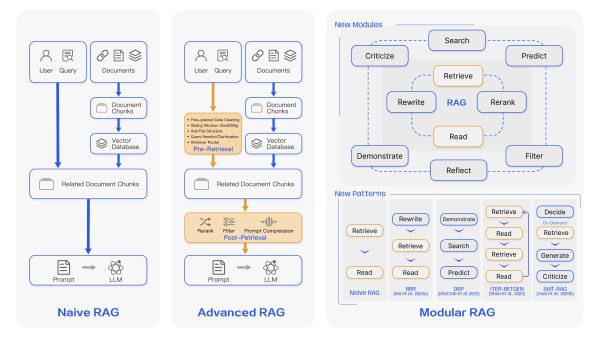
Image credit:Baoyu, Prompt Engineer
By leveraging RAG, businesses can create more intelligent, adaptive, and trustworthy AI systems that drive growth through improved decision-making, enhanced customer experiences, and increased operational efficiency.
RAG-based AI assistantsare opening up new business opportunities by dramatically improving productivity and capabilities compared to traditional large language models (LLMs). RAG allows AI systems to access and leverage large knowledge bases and codebases to provide more accurate, contextual, and useful responses. This creates opportunities for companies to develop specialized AI assistants tailored to specific domains, industries, or enterprise environments.
Cursor AI is another RAG example, this time storing and retrieving a codebase as well as API and library documentation to provide the right context for LLMs to then write new code or edit existing parts of it:
One key business opportunity is in developing advanced context engines and retrieval systems. Having multiple “lenses” or context providers that can quickly pull relevant information from various sources is crucial for RAG performance. Companies that can build high-performance code search indexes, natural language search capabilities, and connectors to different data sources will be well-positioned in this space. There’s also potential for creating industry or domain-specific knowledge bases that can be used to augment general LLMs.
The shift towards agentic workflows enabled by RAG creates opportunities for workflow automation and productivity tools. As the article notes, iterative AI agents that can plan, execute subtasks, and refine their own work produce significantly better results than simple one-shot LLM responses. Businesses could develop specialized agents for tasks like research, coding, writing, or data analysis that leverage RAG to work more autonomously and produce higher quality output. There’s also potential for creating platforms that allow non-technical users to easily create and deploy custom AI agents for their specific needs.
Finally, the need for fast token generation in RAG systems opens up opportunities in AI infrastructure and model optimization. As highlighted, being able to quickly generate many tokens for internal agent reasoning is crucial for these iterative workflows. Companies that can provide high-performance, cost-effective infrastructure for running RAG systems at scale, or develop optimized models that balance speed and quality for RAG use cases, could find significant demand for their solutions as more businesses adopt these technologies.
GraphRAG is a relatively new approach to RAG, using Knowledge Graphs to more effectively store and retrieve connected information. Knowledge Graphs have been used with great success, for example powering Google Search, so combining them with RAG feels like a natural progression.
While GraphRAG offers these significant improvements, it’s important to note that it comes with its own challenges, particularly in terms of computational cost and complexity. The process of creating and maintaining the knowledge graph, including entity extraction, relationship identification, and multi-level summarization, can be significantly more expensive than traditional RAG approaches. Therefore, while GraphRAG presents a promising solution to many RAG limitations, its implementation requires careful consideration of the trade-offs between improved performance and increased computational costs.
In a recent lecture from the Stanford CS25: Transformers United V3 course, Douwe Kiela from Contextual AI shared valuable insights on the current state and future of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. His presentation highlighted several key areas where RAG is making significant strides and where future developments are likely to occur.
Kiela emphasized the substantial performance enhancements that RAG systems bring to language models:
Kiela touched on some ethical implications of RAG systems:
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) represents a significant leap forward in AI technology, combining the power of large language models with the ability to access and utilize external knowledge sources. This hybrid approach addresses many limitations of traditional AI systems, offering improved accuracy, reduced hallucinations, and the ability to work with up-to-date information.
As we’ve explored, RAG systems have wide-ranging applications across various business sectors, from enhancing customer service to revolutionizing research and development processes. The technology’s ability to provide more contextually relevant and factually grounded responses opens up new possibilities for AI-driven solutions in knowledge management, personalized marketing, legal compliance, and beyond.
However, RAG is not without its challenges. Current systems face issues with scalability, contextual understanding, and the complexity of integrating diverse knowledge sources. Emerging solutions like GraphRAG show promise in addressing these limitations by leveraging knowledge graph structures to enhance contextual understanding and relationship mapping.
It’s now hard to imagine a future where some form of RAG technology is not a large part of daily life for millions of people. At the smallest scale, any knowledge worker can now have a truly personal AI assistant. And at the other end of the specturm, governments will have the ability to make more informed and effective decisions, taking advantage of the otherwise overwhelming amount of data they have access to.
For businesses and organizations looking to stay at the forefront of AI technology, understanding and leveraging RAG systems will be crucial. The potential for increased efficiency, improved decision-making, and enhanced user experiences makes RAG a key area to watch and invest in as we move forward in the age of AI-driven innovation.